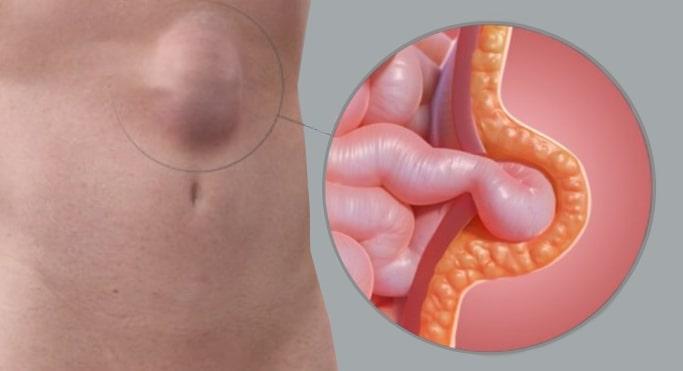
Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery
Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair uses an instrument called a laparoscope. Between two and four small incisions are made through the abdominal wall by which the instruments are inserted to the abdomen.
The incisions are small, so the complete technique cause less scars and pain than open surgery. Laparoscopy is often called keyhole surgery. (Conventional surgery is called open surgery) The hernia is then viewed from inside the abdomen, from the other side of the abdominal wall. The abdominal cavity is inflated with carbon dioxide gas to give the surgeon space to work inside the patient and the actual operating is done remotely with long instruments. The hernia defect or hole is covered with mesh from within the abdomen and staples commonly fired through it into the muscle tissue in order to fix it as a patch.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Hernia Surgery
In this kind of surgery patient has less postoperative discomfort and pain, reduced recovery time that allows earlier return to full activity, easier repair of a recurrent hernia, the ability to treat bilateral hernias concurrently, the performance of a simultaneous diagnostic laparoscopy, ligation of the hernia sac at the highest possible site, improved cosmesis, and decreased incidence of recurrence.

